If you’ve ever wished for a trebuchet that could fire erasers at the cubicles across the aisle–or wished you had the capital to mass produce the one you made in your garage, crowdfunding wants to talk to you. The basic idea behind crowdsourcing, as coined by Jeff Howe in a 2006 article for WIRED, is that a large task can be accomplished by parceling it out among a “network of people in the form of an open call.” Crowdfunding modifies this idea by making the “large task” the production budget of a project. People who answer the call for participation in crowdfunding, called backers, contribute small to large amounts of money so the crowd can collectively raise the needed sum. Yet, “crowds” are, ironically, probably the wrong way to think about what’s happening with crowdfunding in general and its most visible offspring, Kickstarter.com. Rather, Daren Brabham, in his definitive book Crowdsourcing, links crowdfunding success to online communities, calling them “fertile sources of innovation and genius.”
To understand how all of this works, we need to meet Kickstarter. Kickstarter.com hosts projects and campaigns by independent creators, organizing project pitches and facilitating payments. They also lay down rules for what kinds of things can be pitched. Backing typically takes place over a month, overt charities are not allowed, and projects must have a finite endpoint: producing an iSomething accessory, printing a comic book, or turning an abandoned house in New Orleans into a ball pit. Many types of goals and endeavors are therefore collapsed together as projects. Project backers are kept appraised of a project’s progress, consulted for key decisions, and get an exclusive channel to communicate with project creators through the Kickstarter site. Project creators become more committed to a project that they know has generated interest. This process is closer to co-creation, where fans and producers come together with interest and enthusiasm around a shared culture.
Although a Kickstarter campaign invitation is open to anyone browsing the web, it takes a relatively small number of people to make a project successful: all funds donated (minus Kickstarter’s 5% fee) go to the project creator rather than being funneled through a foundation, production company, PayPal, or other edifice of red tape. Kickstarter’s “crowd,” then, is more often an activation of a community or subculture than a random assortment of people on the virtual street. Once we re-frame Kickstarter as invoking community interests rather than those of a faceless crowd, we can start to more clearly think through how crowdfunding works.
Kickstarter.com argues strongly that they are not a store and designs their policies and site to avoid the appearance of being an online storefront. These are obviously muddy waters, particularly as one of Kickstarter’s most notable additions to the traditional investment funding model is a system of “backer rewards.” These rewards vary tremendously from material to immaterial to symbolic to somewhere in-between, and are set up by project creators to thank backers who contribute different tiers of money. Rewards can become an unexpected burden for project creators, who deliver them later than expected over 75% the time. The best rewards are intrinsically linked to the project at hand, rather than being unrelated additions that create unnecessary work rather than deepening the excitement among backers and commitment by creators.
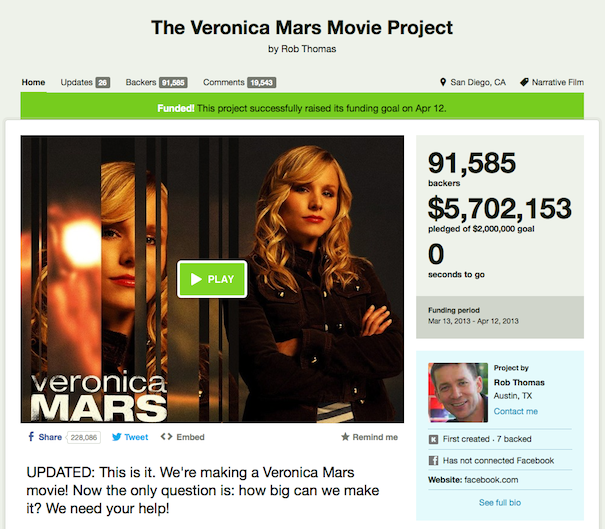
The one particularly dedicated fan who found $10,000 to donate to Rob Thomas’ Veronica Mars Movie campaign, for example, will get a small speaking role in the film. The more modest $10 donation level (selected by a less modest 8,423 people) receive a smaller reward (a digital copy of the film’s shooting script), but one that is still tied to the making of the movie. The Veronica Mars campaign raised the most money of any project, ever, on Kickstarter and ignited both controversy and a lot of useful debate about the crowdfunding model. Today’s hotspot* features Civic Paths members diving into the fray and continuing the crowdfunding conversation.
One theme across posts is to follow the money: Where is it coming from? Where is it going? How does it get there? Why does it go? Kickstarter projects complicate a simple dichotomy of commercial goals vs. creative endeavors, which were previously compartmentalized and personalized by such terms as “fans” and “producers.” According to Samantha Close, Kickstarter lays bare tensions that were always there in the entertainment industry but hidden by layers of production and distribution. Liana Gamber Thompson unpacks the implications of the new Donald Trump-branded site, Fund Anything. In true Trump style, it’s an extreme caricature of crowdfunding where anything goes, from medical procedures to a party for kids displaced by Hurricane Sandy. Its emergence provokes difficult questions about what gets funded and why in the larger crowdfunding world. Despite the prominence of project hosting sites like Kickstarter, all crowdfunding also requires the backing of a payment system. As Lana Swartz reveals, these systems can have politics of their own, resulting in funds being frozen, reducing trust in crowdfunding platforms, and frustrating all participants.
Spreadability, discussion, and debate that bridges communities is another theme of interest. Unlike Surowiecki’s Wisdom of Crowds, where the number of jellybeans in a bowl can be most accurately estimated by taking an average across a large number of observers, there isn’t necessarily a best solution to find in crowdfunding. Rather, projects spark conversations and debates that take place elsewhere, often necessarily as Kickstarter has a fairly strict moderation policy on the site’s discussion sections that, for example, frowns on negative comments. Kevin Driscoll connects projects focusing on saving media with the politics of preservation, noting how debates about stuff are also difficult conversations about what should be archived, how, and by whom. Mike Ananny questions how crowdfunding is being incorporated into news. It troubles existing dynamics of journalism that evolved to promote the spread of meaningful information at the same time as some have taken the cue to openly and explicitly focus on underserved communities. Benjamin Stokes makes the point that feelings of community affiliation are imagined as well as geographically-proximate. Thus, online projects can also directly impact offline civic well-being. However, both Stokes and Ananny point out that there remain significant participation gaps on Kickstarter that affect how networks of privilege are connected to isolated communities, exacerbating the politics of financial support. Andrew Schrock provides examples of success stories in the spread of Hacker and Maker Spaces (HMSs) that act as centers for informal learning and creativity in geographically-situated communities. These democratically-run collective organizations buck the stereotype of HMSs being confined to western male geeks more interested in picking locks than helping others.
Kickstarter’s popularity has brought with it significant controversies and legitimate questions of who gets to contribute, how, to what, and who really benefits in the end. We hope that with careful consideration crowdfunding can be viewed as and truly become a way to connect backers and creators more closely over tables (made of robotically sculpted Zen sand or not) that are meaningful to all parties involved. Crowdfunded projects can drive awareness and, even in their imperfection, spark conversations about what needs doing across various communities. These emergent debates are vital for us to have in this moment of economic transition and cultural shift.
Enjoy, and we welcome your comments.
–Andrew Schrock and Samantha Close
[1] Why All Kickstarters are Civic Kickstarters, by Samantha Close
[2] Donald Trump and Dollar Bills: Crowdfunding for the Masses, by Liana Gamber Thompson
[3] Getting the Funds from the Crowd: The Politics of Payment Infrastructure, by Lana Swartz
[4] Crowdfunding an Archive: What’s Worth Saving and Who’s Gonna Pay for It?, by Kevin Driscoll
[5] Crowd-Funded Journalism and Dynamics of Visibility, by Mike Ananny
[6] Crowdfunding as Neighborhood Storytelling, by Benjamin Stokes
[7] Kickstarting a Hackerspace, by Andrew Schrock
* HOTSPOT PHILOSOPHY: These collections of mini-blog posts — “hot spots” — are organized around themes that cut across the diverse interests of participants in our research group. They’re about the things we love to talk about. And, like our in-person conversations, they play with ideas at the intersection of participatory culture, civic engagement, and new media. Our rules for the hotspot are these: No one gets to spend a million hours wordsmithing — these are idea starters, not finishers — and posts shouldn’t be a whole lot longer than five hundred words. Check out our first hotspot intro to read more about the thought process behind these mini-blog posts.